Acoustic Emission Testing
بازرسی به روش نشر فرآوایی یکی از روش های بازرسی می باشد که با استفاده از امواج صوتی و التراسونیک حاصل از آزادسازی تنش ها، برای شناسایی عیوب در تجهیزات، مخازن، خطوط لوله و همچنین مانیتوریگ و پایش سلامت آنها مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. این امواج اولتراسونیک مانند بازرسی به روش اولتراسونیک معمولی توسط منبع خارجی (پیزوالکتریک) تولید نمی شوند، بلکه از خود تجهیز تحت بازرسی تولید و منتشر می شوند. بازرسی به روش نشر فرآواریی یکی از روش های رایج و مفید بازرسی غیرمخرب می باشد. اولین و مهمترین مزیت بازرسی به روش نشر فرآوایی، این است که به بازرس این اجازه را می دهد تا تجهیزات را تحت بارگذاری و بدون آسیب رساندن به آن و حتی در حین سرویس مورد بازرسی قرار دهد. در گذشته، بازرسی به روش نشر فرآوایی، تنها جهت بازرسی و نگهداری سازه های عظیم و گرانقیمت به سبب هزینه های بالای مربوط به آن استفاده می شد، اما امروزه با پیشرفت تکنولوژی و کاهش هزینه های تجهیزات، بازرسی به روش نشرفرآوایی برای بازرسین قابل دسترس می باشد.


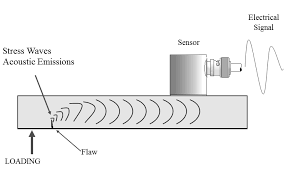
در بازرسی به روش نشر فرآوایی، بازرس امواج اولتراسونیک الاستیک را که در سرتاسر سطح مواد جامد حرکت نموده اند را با استفاده از سنسورهای مخصوص، جمع آوری می نماید. همانطور که امواج اولتراسونیک در سرتاسر سطح حرکت می کند تحت تاثیر عیب، هم سرعت و هم شدت موج، تغییر پیدا می کند و بازرس با نگاه کردن به این تغییرات، عیب را شناسایی می کند. محدوده امواج اولتراسونیکی که معمولا در این بازرسی مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد ۲۰KHz-1MHz می باشد. برای درک بهتر، امواجی را اولتراسونیک گویند که محدوده ی آنها، بیش از حد شنوایی انسان می باشد و امواج نشرفرآوایی، امواجی هستند که به سبب آزادسازی سریع انرژی از منابع متمرکز درون مواد ایجاد می شوند. نشر امواج اکوستیک زمانی اتفاق می افتد که تجهیزات و قطعات تحت تنش یا بارگذاری شدید و یا در دماهای بالا واقع شوند. این انتشار معمولا مربوط به برخی از عیوب یا تخریب های صورت گرفته در ساختار می باشد که این امواج را از خود ساتع می کنند. این امواج می تواند از تغییرات فازی مواد، خوردگی های فعال، تنش های گرمایی، ترک های سرمایشی و یا شکست و جدایش پیوندها و ساختارها باشد.
مهمترین کاربردهای بازرسی به روش نشر فراوایی، عبارتند از بازرسی خوردگی سطحی و حذف پوشش محافظ در مواد، نشتی یابی در خطوط لوله و مخازن ذخیره، عیب یابی خطوط جوش و شناسایی عیوب و تخلیه جزئی قطعات در معرض ولتاژ بالا می باشد. همچنین از این روش برای بازرسی تجهیزات کامپوزیتی تقویت شده با الیاف شیشه نیز استفاده می شود. چند مورد کاربردی از این روش شامل بازرسی پل ها، توربین های بادی، پایش سلامت سازه ها، بازرسی خوردگی مخازن ذخیره و تحت فشار و تخمین طول عمر هواپیماها می باشد.
برای انجام بازرسی، سطح قطعه مورد نظر تمیزکاری می شود و سنسورهای Acoustic Emission بر روی سازه یا تجهیز مورد نظر قرار می گیرند. سنسورها بواسطه اعمال میزان مناسبی از کوپلنت که فضای خالی میان سنسور و سطح قطعه را پوشش می دهد تا از عدم رسیدن امواج به سنسورها جلوگیری کند. پس از اتصال مناسب سنسورها، امواج تنشی موجود در تجهیز را دریافت کرده و به سیگنال های الکتریکی تبدیل می کند که توسط بازرس قابل خواندن می باشد. بازرسان داده های دریافت شده توسط سنسورها را با استفاده از کابل های مخصوصی جمع آوری میکنند و به ردیفی از داده های قابل نمایش بر روی مانیتور تبدیل می کنند. بازرسان جهت شناسایی محل تنش بر روی جسم مورد بازرسی، داده ای که در دسترس است را تفسیر می کنند و به دنبال مکان های احتمالی عیوب ناشی از آن تنش می گردند. تعیین میزان تعداد سنسورهای مورد نیاز جهت بازرسی به عواملی همچون پیچیدگی هندسی، اندازه و نوع قطعات و سازه بستگی دارد.
از مزایای بازرسی به روش نشر فرآوایی می توان به امکان اندازه گیری مستقیم مکانیزم شکست، حساسیت و سرعت بالای تست، بازرسی کل سازه حتی در محیط های خطرناک مانند فشار و دمای بالا و همچنین مونیتورینگ و پایش سلامت آنها از راه دور اشاره کرد. از محدودیت های بازرسی به روش نشر فراوایی نیز می توان به عدم تعیین دقیق محل عیب، حساس بودن به نویز و صداهای محیط اشاره کرد.
باتوجه به کاربرد فراوان بازرسی به روش نشر فراوایی، برای تجهیزات و مواد متفاوت، استاندارهای زیادی در این مورد تدوین شده است که تعدادی از آنها در زیر آورده شده است.
استاندارد های این روش بازرسی:
ASME (AMERICAN SOCIETY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERS)
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code: Section XI, Division 1, Article IWA-2000, Examination and Inspection, (IWA-2234) Acoustic Emission Examination
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code: Section XI, Division 1, Code Case N-471, Acoustic Emission for Successive Inspections
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code: Section XI, Division 1, Code Case No. N-471, Acoustic Emission for successive inspections—Supplement 1 Guidance information for acoustic emission monitoring of pressure boundaries during operation
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code: Section XI, Appendix, Acoustic Emission Monitoring of Nuclear Reactor Pressure Boundaries during Operation
- ASME RTP-1-1995: Standard Guide to Test Methods and Standards for Nondestructive Testing of Advanced Ceramics
ASTM (AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS)
- ASTM C 1175: Standard Guide to Test Methods and Standards for Nondestructive Testing of Advanced Ceramics
- ASTM E 543: Standard Specification for Agencies Performing Nondestructive Testing
- ASTM E 569: Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Monitoring of Structures During Controlled Stimulation
- ASTM E 650: Standard Guide for Mounting Piezoelectric Acoustic Emission Sensors
- ASTM E 749: Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Monitoring During Continuous Welding
- ASTM E 750: Standard Practice for Characterizing Acoustic Emission Instrumentation
- ASTM E 751: Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Monitoring During Resistance Spot-Welding
- ASTM E 976: Standard Guide for Determining the Reproducibility of Acoustic Emission Sensor Response
- ASTM E 1065: Standard Guide for Evaluating Characteristics of Ultrasonic Search Units
- ASTM E 1067: Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Examination of Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic Resin (FRP) Tanks/Vessels
- ASTM E 1106: Standard Test Method for Primary Calibration of Acoustic Emission Sensors
- ASTM E 1118: Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Examination of Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Pipe (RTRP)
- ASTM E 1139: Standard Practice for Continuous Monitoring of Acoustic Emission from Metal Pressure Boundaries
- ASTM E 1211: Standard Practice for Leak Detection and Location Using Surface-Mounted Acoustic Emission Sensors
- ASTM E 1212: Standard Practice for Quality Management Systems for Nondestructive Testing Agencies
- ASTM E 1316: Standard Terminology for Nondestructive Examination
- ASTM E 1359: Standard Guide for Evaluating Capabilities of Nondestructive Testing Agencies
- ASTM E 1419: Standard Practice for Examination of Seamless, GasFilled, Pressure Vessels Using Acoustic Emission
- ASTM E 1495: Standard Guide for Acousto-Ultrasonic Assessment of Composites, Laminates, and Bonded Joints
- ASTM E 1544: Standard Practice for Construction of a Stepped Block and Its Use to Estimate Errors Produced by Speed-ofSound Measurement Systems for Use on Solids
- ASTM E 1736: Standard Practice for Acousto-Ultrasonic Assessment of Filament-Wound Pressure Vessels
- ASTM E 1781: Standard Practice for Secondary Calibration of Acoustic Emission Sensors
- ASTM E 1888 / E 1888 M: Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Examination of Pressurized Containers Made of Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic with Balsa Wood Cores
- ASTM E 1930: Standard Practice for Examination of Liquid-Filled Atmospheric and Low-Pressure Metal Storage Tanks Using Acoustic Emission
- ASTM E 1932: Standard Guide for Acoustic Emission Examination of Small Parts
- ASTM E 2075 / E 2075M: Standard Practice for Verifying the Consistency of AESensor Response Using an Acrylic Rod
- ASTM E 2076 / E 2076 M: Standard Practice for Examination of Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic Fan Blades Using Acoustic Emission
- ASTM E 2191 / E 2191 M: Standard Practice Method for Examination of Gas-Filled Filament-Wound Composite Pressure Vessels Using Acoustic Emission
- ASTM E 2374: Standard Guide for Acoustic Emission System Performance Verification
- ASTM E 2478: Standard Practice for Determining Damage-Based Design Stress for Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Materials Using Acoustic Emission
- ASTM E 2533: Standard Guide for Nondestructive Testing of Polymer Matrix Composites Used in Aerospace Applications
- ASTM E 2598: Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Examination of Cast Iron Yankee and Steam Heated Paper Dryers
- ASTM E 2661 / E 2661M: Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Examination of Plate-like and Flat Panel Composite Structures Used in Aerospace Applications
- ASTM E 2863 / E 2863M: Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Examination of Welded Steel Sphere Pressure Vessels Using Thermal Pressurization
- ASTM E 2907: Standard Practice for Examination of Paper Machine Rolls Using Acoustic Emission from Crack Face Rubbing
- ASTM F 914 / F 914 M: Standard Test Method for Acoustic Emission for Aerial Personnel Devices Without Supplemental Load Handling Attachments
- ASTM F 1430 / F 1430 M: Standard Test Method for Acoustic Emission Testing of Insulated and Non-Insulated Aerial Personnel Devices with Supplemental Load Handling Attachments
- ASTM F 1797: Standard Test Method for Acoustic Emission Testing of Insulated and Non-Insulated Digger Derricks
- ASTM F 2174: Standard Practice for Verifying Acoustic Emission Sensor Response
- ASTM E 2374: Standard Guide for Acoustic Emission System Performance Verification
CEN (EUROPEAN COMMITTEE FOR STANDARDIZATION)
- CEN EN 1071-3 2005: Advanced technical ceramics – Methods of test for ceramic coatings – Part 3: Determination of adhesion and other mechanical failure modes by a scratch test
- CEN EN 1330-1 1998: Non-destructive testing – Terminology – Part 1: List of general terms
- CEN EN 1330-2 1998: Non-destructive testing – Terminology – Part 2: Terms common to the non-destructive testing methods
- CEN EN 1330-9 2009: Non-destructive testing – Terminology – Part 9: Terms used in acoustic emission testing
- CEN EN 12817: 2010: LPG Equipment and accessories – Inspection and requalification of LPG tanks up to and including 13 m³
- CEN EN 12819 2009: LPG equipment and accessories – Inspection and requalification of LPG tanks greater than 13 m³
- CEN ISO/TR 13115 2011: Non-destructive testing – Methods for absolute calibration of acoustic emission transducers by the reciprocity technique (ISO/TR 13115:2011)
- CEN EN 13445-5 2009: Unfired pressure vessels – Part 5: Inspection and testing (Annex E)
- CEN EN 13477-1 2001: Non-destructive testing – Acoustic emission – Equipment characterization – Part 1: Equipment description
- CEN EN 13477-2 2010: Non-destructive testing – Acoustic emission – Equipment characterization – Part 2: Verification of operating characteristic
- CEN EN 13554 2011: Non-destructive testing – Acoustic emission – General principles
- CEN EN 13480-5 2012: Metallic industrial piping – Part 5: Inspection and testing
- CEN EN 14584 2013: Non-destructive testing – Acoustic emission – Examination of metallic pressure equipment during proof testing – Planar location of AE sources
- CEN EN 15495 2007: Non Destructive testing – Acoustic emission – Examination of metallic pressure equipment during proof testing – Zone location of AE sources
- CEN EN 15856 2010: Non-destructive testing – Acoustic emission – General principles of AE testing for the detection of corrosion within metallic surroundings filled with liquid
- CEN EN 15857 2010: Non-destructive testing – Acoustic emission – Testing of fibre-reinforced polymers – Specific methodology and general evaluation criteria
- CEN EN ISO 16148 2006: Gas cylinders – Refillable seamless steel gas cylinders – Acoustic emission testing (AT) for periodic inspection (ISO 16148:2006)
- CEN ISO/TR 25107 2006: Non-destructive testing – Guidelines for NDT training syllabuses (ISO/TR 25107:2006)
- CEN CR 13935 2000: Non-destructive testing – Generic NDE data format model

